Applied Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) courses typically cover topics that educate students in four specific disciplines — science, technology, engineering and mathematics — in an interdisciplinary and applied approach. STEM becomes STEAM when the Arts are incorporated into the classroom. Usually these courses contain a breadth of content from various disciplines, making them difficult to classify.
Career Technical Education (CTE) vs. General Education
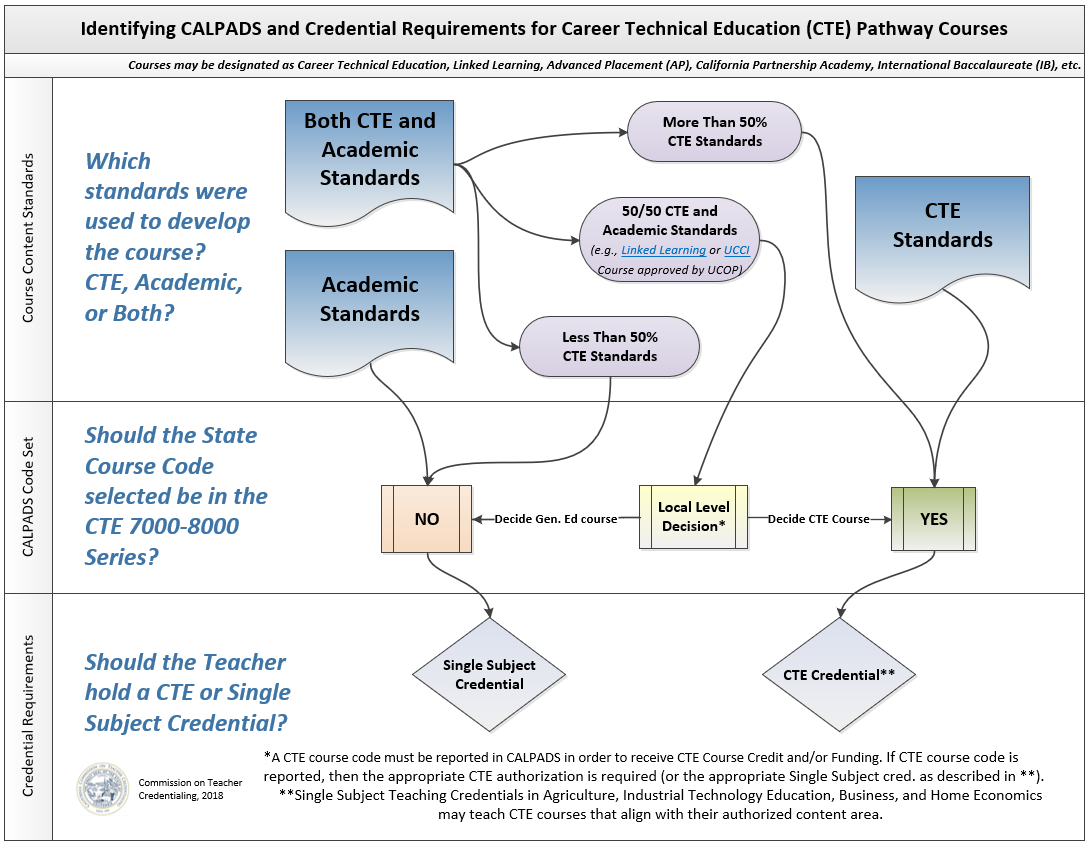
In addition to being interdisciplinary, it may also be difficult to distinguish whether a STEM course is more appropriately classified as a Career Technical Education or General Education Course, especially if the course was developed using both CTE and academic standards. The following flowchart can assist in determining whether the STEM class should be staffed by a Single Subject or CTE credential holder:
Additionally, Education Code §51225.3(b) provides that LEAs may offer graduation credit through alternative courses of study, including CTE classes. However, be mindful that this section of statute requires that pupils, parents, teachers, and the public be notified of alternative modes of completing prescribed courses of study.
If a STEM course is in a CTE setting, it will need to be coded as a CTE course in CALPADS. These courses are in the 7000-8000 series of the course codes.
Assignment Monitoring for General Education STEM Courses
In CALPADS, the description for the Applied Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Course (Course Code #9222) is as follows:
“Applied Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) courses typically cover topics that educate students in four specific disciplines — science, technology, engineering and mathematics — in an interdisciplinary and applied approach. STEM courses present students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge in hands-on activities.”
Course Code #9222 should be reported for STEM courses in conjunction with specific content subcategories in order to help further identify the focus of the course. See below for a list of the content subcategories available in CALPADS, and the possible course content areas touched on in these subcategories.
| Content Subcategory | Possible Content Areas Covered |
|---|---|
| Aeronautics |
|
| Application Development |
|
| Architecture |
|
| Computer Science Applications |
|
| Design and Modeling |
|
| Electricity and Electrons |
|
| Energy and the Environment |
|
| Medical Exploration |
|
| Robotics |
|
| Technology |
|
| Engineering |
|
| Multiple or Not Applicable | Multiple:
Not applicable:
|
In the content subcategory areas listed above, the Commission will code them to ALL possible disciplines involved, and therefore, multiple appropriate credential authorizations.
For example: Engineering is not subsumed under any one single science subject area, but components of it may be found in a few different areas such as Physics, ITE, and even Mathematics. Therefore, the course content subcategory code will be coded to accept all of these credential authorizations in CalSAAS. If the educator holds any one of them, no exception will be triggered.
Because of this, there is still going to be flexibility for LEAs to choose the content of the course, as they are ultimately responsible for determining the true course content in these types of interdisciplinary assignments. However:
- If the focus of the course is more than 50% comprised of one discipline, we consider that primary content area and driver of the assignment. In this scenario the educator should be credentialed accordingly;
- If the content is equally distributed between two or more disciplines, then the educator should be appropriately authorized to teach each discipline.
Again, CalSAAS will consider any of the multiple appropriate credential authorizations for these content subcategories in order to afford the LEAs autonomy and flexibility. However, because of this leeway, the monitoring authority should take special care when evaluating these assignments.
.png?sfvrsn=c28b72b1_10)
.png?sfvrsn=cd8b72b1_0)